Case Study: How StarColor Flexographic Ink Transforms Napkin Printing
Date: Sep 17 2025 From: Star Color Views:
Napkin printing must not only ensure attractive colors and clear patterns but also meet three core requirements: food safety, environmental compliance, and cost control. Traditionally, napkin printing has relied on solvent-based flexographic inks, which suffer from high VOC emissions, excessive solvent residues, and low printing precision. Particularly in food-contact applications, these drawbacks have created significant safety risks and regulatory pressures, becoming a bottleneck for the industry.
StarColor’s water-based flexographic inks, designed specifically for paper substrates, leverage a “low-migration formulation + high process adaptability” to fundamentally resolve these issues. Already adopted at scale by multiple napkin manufacturers, this case study examines how StarColor inks reshape technical standards and market value in the napkin printing industry.
I. Industry Pain Points: Limitations of Traditional Inks
Before adopting StarColor inks, napkin printing companies commonly faced three major challenges that constrained product quality and compliance:
-
Food Safety Risks
Napkins often come into direct contact with food. Solvent-based inks contain aromatic and ester solvents that can remain in paper fibers and migrate into food.
-
Tests show that napkins printed with traditional inks had solvent residue levels of 8.2 mg/m² at 40°C under simulated food-contact conditions—well above the China GB 4806.8-2016 limit of ≤5 mg/m².
-
Some products even contained trace heavy metals (lead 0.008 mg/kg). While not exceeding official limits, such findings raised consumer concerns and drove up complaint rates.
-
Environmental Compliance Pressure
Stricter environmental policies have made the high emissions of solvent-based inks unsustainable.
-
For a company producing 1 million napkins per day, VOC emissions reached 120 kg daily.
-
To comply, the company had to operate costly RTO (regenerative thermal oxidizer) systems, with annual operating expenses of about USD 50,000.
-
Secondary pollutants from RTO added further compliance risks, a heavy burden for small and mid-sized firms.
-
Printing Quality Challenges
Due to the low density (0.3–0.5 g/cm³) and high absorbency of napkin paper, solvent inks caused issues such as show-through, dot gain, and uneven color:
-
50% dot gain often exceeded 20%, making fine patterns (<4pt) blurry.
-
Batch color differences frequently exceeded ΔE 1.5, failing to meet brand requirements.
-
Slow drying (3–5 seconds at 60°C) led to smudging during rewinding, pushing waste rates to 10–12%, far higher than the industry ideal of 3–5%.
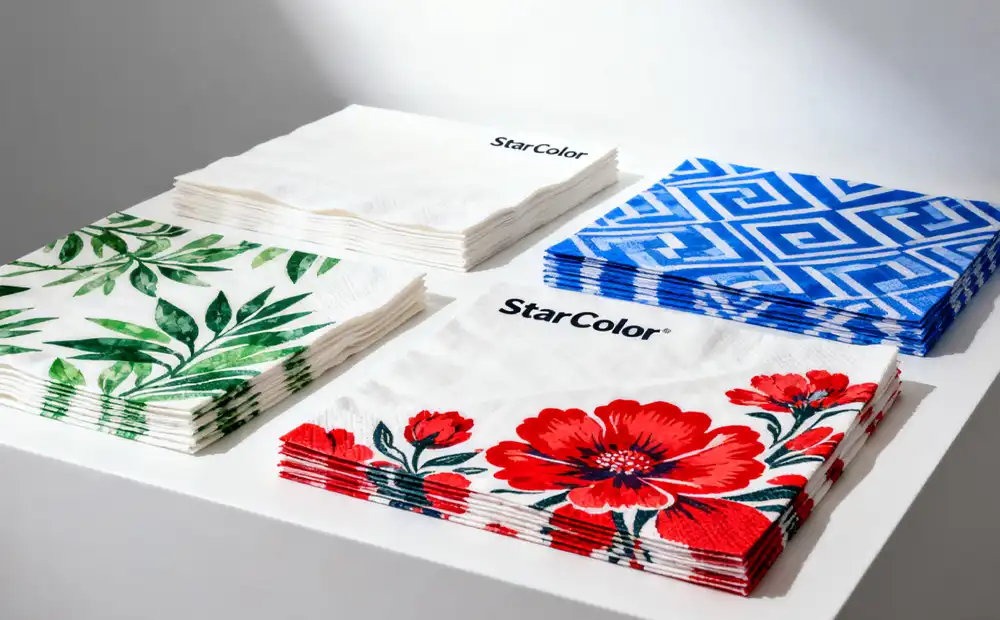

II. StarColor Flexographic Ink: Technical Breakthroughs
StarColor inks address both substrate-specific challenges and industry demands through formulation innovation and process optimization, offering three key advantages:
-
Food Safety Upgrade
-
Safe raw materials: Formulated with FDA 21 CFR 175.300 compliant acrylic resins, organic pigments free of detectable heavy metals (<0.001 mg/kg), and no benzene/ketone solvents. Instead, deionized water and ≤5% food-grade ethanol are used, reducing VOC levels to 30 g/L (just 1/10 of traditional inks).
-
Migration testing: In GB 31604.1-2015 tests with 4% acetic acid and isooctane, specific migration was ≤0.01 mg/kg and overall migration ≤15 mg/dm², well below limits. Solvent residues were just 1.2 mg/m².
-
Sensory quality: Napkins passed odor transfer testing (40°C, 24h with water) with no detectable smell, fully meeting food-contact standards.
-
Environmental and Cost Benefits
-
Low VOC emissions: At only 30 g/L, VOCs fall well below regulatory thresholds. Companies can meet standards with simple activated carbon systems, cutting annual treatment costs to under USD 7,000—an 85% savings compared to RTO.
-
Ink recycling: Unused ink can be stored for 7 days and reused after filtration, boosting ink utilization from 85% to 95% and saving about USD 16,000 annually.
-
Printing Quality Enhancement
-
Optimized substrate compatibility: Adjusting solids (45–50%) and viscosity (18–22s, #4 cup, 25°C) minimized deep penetration, reducing show-through from 30% to below 5%. Specialized leveling agents improved surface smoothness by 40%.
-
Higher precision and color stability: Nano pigment dispersion and controlled dot gain (8–10%) allowed crisp 3pt text and 150 lpi halftones. Batch color variation dropped to ΔE ≤0.8, improving brand consistency by 60%.
-
Durability: Polyethylene wax (3–4%) reduced surface friction (0.6 → 0.3) and raised rub resistance from 150 to 400 cycles under 500g load. Elongation at break reached 15%, preventing cracking after 100 folds.
III. Case Study: Large Southeast Asian Napkin Producer
1. Background
A large tissue producer (daily output: 1.5 million napkins) struggled with:
-
Solvent residue at 6.8 mg/m² (above limits).
-
VOC concentration of 110 mg/m³, triggering enforcement action.
-
11% waste rate, blurred logos, and a 7% return rate, costing over USD 70,000 annually.
2. Solution
-
Ink selection: StarColor SC-6000 food-grade water-based flexo inks, customized in red, yellow, and blue.
-
Process optimization:
-
Anilox roller: 800 lpi, 6 BCM.
-
Ink layer: 1.2–1.5 μm.
-
Drying: reduced to 45°C, 1.5s.
-
Printing speed: raised from 180 to 250 m/min.
-
-
Quality assurance: Full QC system with solvent residue, ΔE, and rub-resistance testing per batch.
3. Results
-
Food safety compliance: Residues fell to 1.1 mg/m²; migration fully compliant; certified by SGS. Customer complaints dropped from 7% to 0.3%, boosting orders by 20%.
-
Environmental compliance: VOCs dropped to 45 mg/m³, meeting the 80 mg/m³ limit without RTO. Activated carbon systems cut annual environmental costs by USD 42,000.
-
Productivity gains: Waste rates fell from 11% to 3.5%; logo clarity reached 100%. Speed gains of 39% raised daily output to 2.2 million napkins, adding over USD 110,000 in annual revenue.
-
Cost savings: Ink utilization +10%; drying energy cut 70%. Combined savings totaled USD 63,000 annually.
IV. Conclusion: StarColor’s Future Potential
With rising consumer demand and tightening environmental regulations, the napkin printing industry is shifting from low-cost mass production to high-quality, sustainable manufacturing. StarColor flexographic inks, through targeted innovation, have become a crucial enabler of this transformation.
As formulations evolve and compatibility extends to ultra-thin and specialty fibers, StarColor inks are poised to expand into broader paper-based packaging markets.
For napkin producers, adopting StarColor inks is not just about changing ink brands—it is about upgrading production systems, reducing costs, and redefining product value. By combining compliance, quality, and efficiency, StarColor inks help companies gain a competitive edge and achieve sustainable growth.
 RU
RU EN
EN CN
CN















